9 May 2023
- 18 Comments
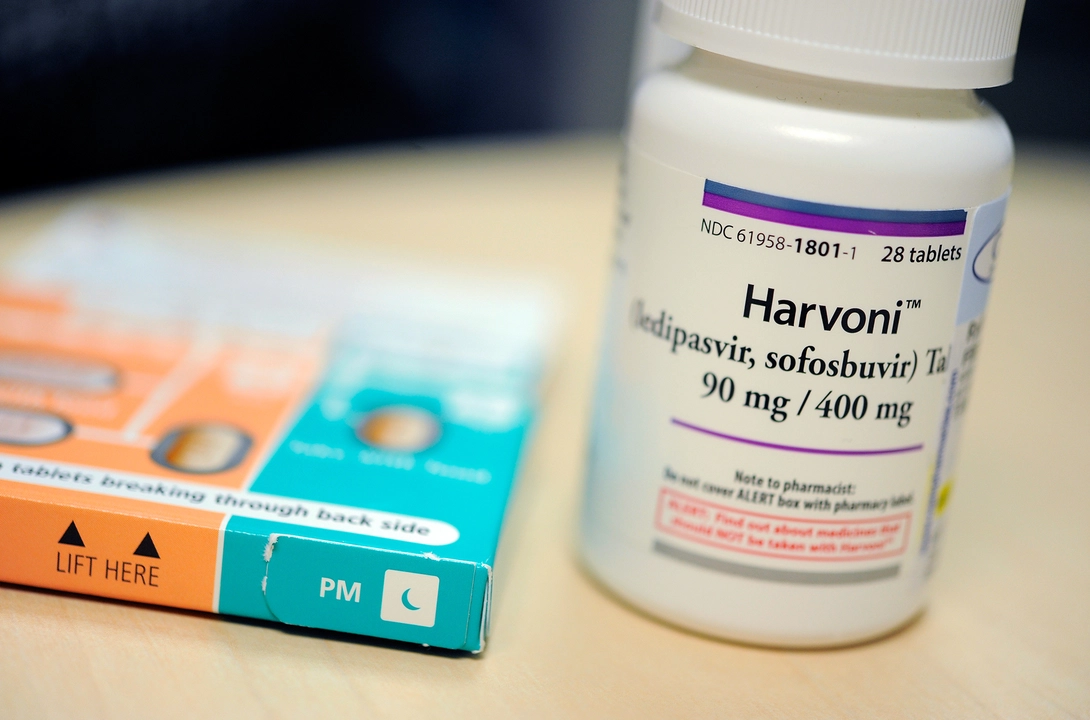
Introduction to Sofosbuvir
As a blogger who is passionate about public health and medical breakthroughs, I was excited to learn about the role of sofosbuvir in treating acute hepatitis C infection. Sofosbuvir is a relatively new antiviral medication that has been shown to be highly effective in treating patients with hepatitis C. In this article, we will dive into the various aspects of sofosbuvir, its mechanism of action, and its significance in the management of acute hepatitis C infection.
Understanding Acute Hepatitis C Infection
Before we discuss the role of sofosbuvir in treating acute hepatitis C infection, it is essential to understand the nature of this viral disease. Hepatitis C is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). In the acute stage of the disease, symptoms may be mild or even nonexistent, making it difficult to diagnose. However, if left untreated, acute hepatitis C can progress to a chronic infection. This can lead to liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even liver failure.
Sofosbuvir's Mechanism of Action
Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide analogue that works by inhibiting the HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme. This enzyme is crucial for the replication of the virus in the liver cells. By blocking the action of this enzyme, sofosbuvir effectively stops the replication process and prevents the virus from multiplying. As a result, the viral load in the body decreases, leading to the eventual clearance of the virus.
Effectiveness of Sofosbuvir in Acute Hepatitis C Treatment
Several clinical trials have evaluated the efficacy of sofosbuvir in the treatment of acute hepatitis C infection. These studies have shown that sofosbuvir, when used in combination with other antiviral medications, can lead to high rates of sustained virologic response (SVR). SVR is defined as the absence of detectable HCV RNA in the blood 12 to 24 weeks after completing treatment, which is considered a cure for hepatitis C infection. The high SVR rates achieved with sofosbuvir-based regimens indicate that this drug is highly effective in treating acute hepatitis C infection.
Advantages of Sofosbuvir-Based Regimens
One of the significant advantages of sofosbuvir-based regimens is the shorter treatment duration compared to older treatment options. Traditional treatments for hepatitis C, such as interferon and ribavirin, often required long treatment durations of up to 48 weeks. In contrast, sofosbuvir-based regimens can achieve high SVR rates in as little as 8 to 12 weeks of treatment. Additionally, sofosbuvir-based regimens have fewer side effects compared to older treatments, making them a more tolerable option for patients.
The Impact of Sofosbuvir on Liver Transplantation
Acute hepatitis C infection, if left untreated, can progress to severe liver damage and even liver failure. In such cases, liver transplantation may be the only life-saving option. However, the availability of sofosbuvir has revolutionized the management of acute hepatitis C infection by preventing the progression of the disease to advanced stages. Consequently, the need for liver transplantation has significantly reduced, helping to save both lives and healthcare resources.
Cost-Effectiveness of Sofosbuvir
Although sofosbuvir is a relatively expensive medication, its high efficacy, shorter treatment duration, and reduced need for liver transplantation make it a cost-effective option for treating acute hepatitis C infection. Additionally, the price of sofosbuvir has decreased over the years, making it more accessible to patients worldwide. The long-term health benefits and potential cost savings from preventing liver-related complications also contribute to the cost-effectiveness of sofosbuvir.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite the numerous advantages of sofosbuvir, there are still some limitations and challenges associated with its use. One of the main concerns is the development of resistance to sofosbuvir, which can occur when the virus mutates and becomes less susceptible to the drug. However, resistance is relatively rare, and the risk can be minimized by using sofosbuvir in combination with other antiviral medications. Another challenge is the accessibility of sofosbuvir, especially in low-income countries where the high cost of the medication may be prohibitive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sofosbuvir has revolutionized the treatment of acute hepatitis C infection with its high efficacy, shorter treatment duration, and improved safety profile. Its use has significantly reduced the need for liver transplantation and has the potential to prevent liver-related complications. Despite some limitations and challenges, sofosbuvir remains a crucial component in the management of acute hepatitis C infection and offers hope for a future where hepatitis C is no longer a significant public health burden.

Leia not 'your worship'
May 9, 2023I just feel like we're so quick to celebrate pharmaceutical miracles without asking who really benefits. Sofosbuvir? Sure, it cures hepatitis C. But who gets to take it? The people who need it most? Or the ones who can afford the co-pay and the insurance loophole? I mean, it's beautiful science... but it's also capitalism in a pill.
And don't even get me started on the 'cost-effective' narrative. That's just corporate speak for 'we'll make it cheaper after we've already maxed out the profits.'
Jo Sta
May 10, 2023This is why America's healthcare system is a joke. You spend billions developing a cure, then price it like a luxury watch. Meanwhile, people in other countries are dying because they can't get the damn drug. If this was a vaccine for a white person's disease, it'd be free at every Walmart.
KALPESH GANVIR
May 11, 2023I'm from India, and I've seen firsthand how hard it is to get even basic meds. But I'm glad the price of sofosbuvir dropped. My cousin was cured last year with a generic version. It wasn't perfect-side effects were rough-but he's alive now. That's more than most get.
Maybe we don't need to glorify the drug. Just make sure no one gets left behind.
April Barrow
May 13, 2023The data on SVR rates with sofosbuvir is solid. 95%+ across multiple trials. Treatment duration reduced from 48 weeks to 8-12. Side effect profile significantly improved over interferon. The science is clear. The moral question is separate.
Melody Jiang
May 14, 2023It's funny how we treat medical breakthroughs like they're magic. We don't praise the chemist who spent 12 years in a lab. We don't thank the nurses who monitored patients through the trials. We just say 'oh wow, this pill cures hepatitis' and move on.
Maybe the real miracle isn't the drug-it's the quiet, relentless work of people nobody sees.
alex terzarede
May 15, 2023Resistance is rare but real. I've seen cases where genotype 3 with prior treatment failure developed NS5B mutations. Combination therapy reduces risk, but we need better surveillance. Also, drug interactions with HIV meds are underreported. Need more real-world data.
Dipali patel
May 16, 2023EVERYTHING IS A LIE. SOFOSBUVIR WAS DESIGNED BY PHARMA TO MAKE YOU DEPENDENT. THEY KNOW THE VIRUS CAN BE CURED WITH HERBS AND SUNLIGHT. THEY JUST DON'T WANT YOU TO KNOW BECAUSE THEY MAKE BILLIONS OFF CHRONIC TREATMENT. THE FDA IS IN BED WITH BIG PHARMA. THE WHO TOO. THEY WANT YOU TO THINK YOU NEED THIS DRUG WHEN YOU REALLY JUST NEED TO EAT MORE BROCCOLI AND STOP WATCHING TV.
MY COUSIN GOT HEALD BY JUST DRINKING LEMON WATER FOR 3 MONTHS. THEY LOCKED HIM IN A HOSPITAL AND FORCED THE DRUG ON HIM. HE'S STILL TRAUMATIZED.
Jasmine L
May 18, 2023Honestly? I'm just glad we have something that works 😊
My uncle was on interferon back in 2010. He lost all his hair, cried every day, and still didn't clear it. Now? 12 weeks. No hair loss. No depression. Just... better. I don't care if it's expensive-I care that people live.
Also, generics exist now. Don't give up hope.
lisa zebastian
May 19, 2023Sofosbuvir is a Trojan horse. The real goal is to replace all natural immunity with synthetic pharmaceutical dependency. Once you're on it, you're conditioned to believe only corporations can heal you. Next thing you know, your body forgets how to fight viruses on its own. They're not curing you-they're reprogramming you.
Jessie Bellen
May 20, 2023This is why you can't trust doctors. They just push pills. No one talks about the real cause-environmental toxins. Your liver doesn't get hepatitis C from a needle. It gets it from the water you drink and the air you breathe. This drug just masks it.
Jasmine Kara
May 20, 2023sofosbuvir is kinda wild tbh i had no idea it was this effective like i thought it was just another drug but the cure rates are insane and honestly i feel like we're living in the future
Richie Lasit
May 21, 2023Let me tell you something-this is hope in a capsule. I used to work in a needle exchange program. I saw guys come in with cirrhosis, scared, broken. Now? They walk in, get tested, get a script, and come back three months later smiling. No more waiting. No more suffering. This isn't just medicine. It's dignity.
Yeah, it's pricey. But we can fix that. We have to.
arthur ball
May 21, 2023I just wanna say-this is the kind of thing that makes me believe in humanity again. Like, imagine if we treated EVERY disease like this? Not just the profitable ones. What if we poured this energy into malaria? Into TB? Into mental health? The tech exists. The will doesn't.
But hey. One win at a time. Sofosbuvir? Yeah. We did good.
Harrison Dearing
May 23, 2023I get the cost complaints. But here’s the thing: if you had a child with hepatitis C and had to choose between paying $80K for a cure or watching them die… you’d pay it. No debate. The system’s broken, sure. But this? This is the light at the end of the tunnel. Don’t throw it out because the tunnel’s dark.
Justice Ward
May 23, 2023Sofosbuvir is like a symphony for the liver. Every molecule plays its part-precision, timing, harmony. It doesn’t just kill the virus. It gives the organ space to breathe again. I’ve seen livers regenerate after years of damage. It’s not magic. It’s biology doing what it was meant to do… with a little help from science.
bhuvanesh kankani
May 24, 2023In India, we have generic versions available at less than $10 per course. The global community must ensure equitable access. Science should not be a privilege. The Indian pharmaceutical industry has shown that affordability and efficacy can coexist. Let us not forget that.
Iris Schaper
May 25, 2023I think we're missing the bigger picture. Hepatitis C isn't just a virus. It's a symptom. Of poverty. Of incarceration. Of homelessness. Of stigma. We treat the infection like it's the problem. But the problem is the world that lets people get infected in the first place. Sofosbuvir fixes the symptom. We still haven't fixed the cause.
katerine rose
May 25, 2023I got cured with sofosbuvir and I dont even know how i got it i just woke up one day with it and now im fine and im so grateful but also kinda mad i wasted 3 years thinking i was dying